Clinical significance of 13 syphilis detection methods
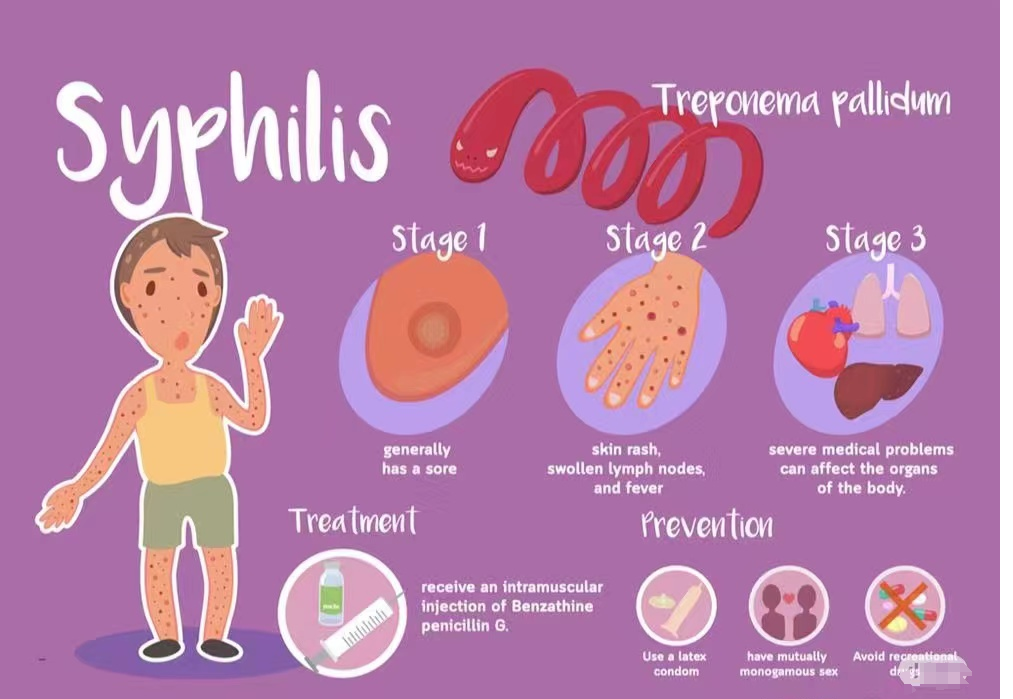
Treponema pallidun (TP) belongs to the pale subspecies of Treponema pallidum in the genus Treponema and is the pathogen that causes human syphilis. The course of syphilis is divided into 3 stages.

Primary syphilis: The main symptom is the occurrence of chancre at the site of invasion, which then disappears when the body develops an immune response to it.
Secondary syphilis: TP spreads with the blood circulation, causing damage to multiple parts and various lesions, at which time the Treponema pallidum multiplies in the body. Primary and secondary syphilis are highly contagious.
Tertiary (late) syphilis: Treponema pallidum invades the nervous system and cardiovascular system, causing great damage, and gumma will occur in multiple organs. This stage is not highly contagious, and the amount of syphilis in the body is extremely small, making it difficult to detect. For example, during the neurosyphilis stage, the most effective detection method currently uses the Toluidine Red Unheated Serum Test (TRUST) method to detect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What are the commonly used detection methods for syphilis?
1 Direct method for detecting syphilis
01 Dark field microscopy (DFM)
DFM can directly observe the syphilis spirochetes in the lesion secretions and is an effective method for diagnosing early syphilis, but the sensitivity of DFM is often low, and because the morphology of syphilis spirochetes is very similar to that of treponema pallidum, treponema inflexum and treponema ulcerans, which are often distributed in the oral and rectal areas, it is not easy to distinguish, so it is not suitable for oral and rectal lesion samples.
02 Direct immunofluorescence test (DFA)
DFA has a higher positive rate than dark field microscopic observation, and can also examine pathological tissue sections, but this method has high technical requirements for experimental personnel and has not yet been widely used in laboratories.
03 Dynamic focus microscopy (FFM)
The principle of FFM is to perform three-dimensional stereoscopic scanning of tissues by moving the focus of the microscope, so that extremely small amounts of spirochetes can be detected, especially for the extremely difficult to diagnose secondary and tertiary syphilis, with detection rates of 97% and 87% respectively.
However, the use of FFM is not popular and the instrument is relatively expensive. Therefore, this method is suitable for the final confirmatory test, especially for the detection of tertiary syphilis.
2 Serological tests for syphilis
01 Non-syphilis Treponema serological tests
Non-syphilis Treponema serological tests include the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test (VDRL), the unheated serum reagin test (USR), the rapid plasma reagin paper test (RPR), and the toluidine red unheated test (TRUST). The main clinical significance is:
1) RPR and TRUST are modified versions of the VDRL test, among which the TRUST method is the simplest and fastest and has better test results, with a positive detection rate of up to 85%.
2) RPR and TRUST are widely used in clinical practice. They are currently often used for screening syphilis, testing the titer of syphilis patients after treatment, and observing the efficacy.
3) According to literature reports, VDRL is a test mainly used to detect cerebrospinal fluid reagin, which is of great value for the diagnosis of neurosyphilis.
4) The above non-treponemal serological tests are mostly used to detect nonspecific antibodies. Nonspecific antibodies often appear later than treponemal specific antibodies. Generally, they can only have good diagnostic efficacy 4 weeks after the appearance of chancre. Therefore, they are not conducive to the differential diagnosis of early syphilis and are very likely to have false negatives and lead to missed diagnosis.
5) The above methods are prone to biological false positive reactions. For example, immune system diseases, infectious diseases, rubella, pneumonia, tumors or pregnancy reactions in pregnant women can cause false positive reactions in such tests. However, the antibody titer of false positive reactions is low, generally rarely exceeding 1:8. Therefore, when positive, it is best to confirm it with treponemal serological tests and identify it with clinical manifestations.
02 Treponema pallidum serological tests
1) Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption Test (FTA-ABS)
The FTA-ABS method is considered the "gold standard" for syphilis testing. It has the characteristics of high specificity and strong sensitivity. It can be used as a confirmatory test for syphilis, but it will have false positives for neurosyphilis with HIV infection.
2) Treponema pallidum hemagglutination test (TPHA) and Treponema pallidum particle agglutination test (TPPA)
TPHA and TPPA are basically similar in principle. TPPA is a modified version of TPHA. Rose-red gelatin particles are used to replace the red blood cells used in TPHA, making the results easier to observe with the naked eye. Both methods have high sensitivity for syphilis detection at all stages and are mostly used to confirm positive results of syphilis screening.
Studies have shown that TPPA has a high detection rate for primary, secondary and tertiary syphilis, but once syphilis is infected, antibodies will exist in the patient's body for life. Therefore, this type of method is generally used as a confirmatory test for past infection with Treponema pallidum and is not suitable for large-scale screening tests.
3) Indirect immunoassay
Indirect immunoassays such as enzyme immunoassay (EIA), syphilis enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (TP-ELISA), chemiluminescence analysis (CLIA), etc. can achieve the effect of signal amplification through different luminescence technologies, so the syphilis detection rate of this type of method can be greatly improved.
However, in terms of specificity, since this type of method is based on the principle of antigen-antibody binding, it is more suitable for the detection of secondary syphilis, and the detection effect for primary syphilis is not ideal.
4) Colloidal gold method
The colloidal gold method has high selectivity in identifying Treponema pallidum-specific antibodies, and the diagnostic cycle is short. Generally, the results can be obtained in 5-15 minutes. It has the advantages of simple operation and strong repeatability. It is suitable for individual screening in primary medical institutions or batch screening of samples in medical units. However, the colloidal gold method will produce false negative reactions when the concentration of specific Treponema pallidum antibodies is too low, resulting in missed detection.
5) Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
This method relies on microscopic examination, so its positive detection rate can only reach 67% at most. However, the combined use of immunohistochemistry and FFM can greatly improve the detection rate.
3 Treponema pallidum nucleic acid amplification detection technology
Currently, Treponema pallidum nucleic acid amplification detection technology (NAAT) mainly includes conventional PCR, multiplex PCR, real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, reverse transcription PCR and nested PCR. The specificity of NAAT for detecting TP is very high (90%~100%), but different types of clinical samples will directly affect the sensitivity of nucleic acid detection.
The clinical significance of NAAT for detecting syphilis:
1) The sensitivity of NAAT for blood components (including whole blood or plasma serum) of patients with primary and secondary syphilis and latent syphilis is extremely low, which can be as low as 0, and the range of variation is large.
2) NAAT has high sensitivity for pregnant women's amniotic fluid, newborn blood and cerebrospinal fluid, and can be used as one of the important bases for the diagnosis of congenital syphilis after optimization.
3) There are many uncertain factors affecting the results of serological tests for the window period of very early antibody production in primary syphilis, neurosyphilis and congenital syphilis. Nucleic acid testing can be combined for auxiliary diagnosis, but the selection of samples should be focused on to improve the detection efficiency of TP.
4) Studies have found that the PolyA gene of Treponema pallidum has very high interspecies specificity. Designing specific detection primers based on the PolyA gene sequence can improve the credibility of the test results. Experiments have shown that the sensitivity and specificity of conventional PCR detection methods using PolyA genes can reach 95%. However, due to non-specific amplification and poor amplification conditions, ordinary PCR cannot guarantee 100% credibility.
5) Nested PCR has much higher sensitivity and specificity than ordinary PCR, and plays an important role in screening false negative samples, but due to its complex operation, it is only suitable as an auxiliary means of detection.
6) Although real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR has high specificity and sensitivity, its sensitivity will be interfered by different samples. If there are substances that inhibit Taq enzyme activity in whole blood, its sensitivity will be reduced, thereby affecting the positive detection rate. The sensitivity of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR for patients with primary syphilis is much higher than that for patients with secondary and tertiary stages. Therefore, the real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR method is more suitable for rapid detection of patients with early syphilis.
Summary
Syphilis has a long onset period, and there is an asymptomatic incubation period between each stage of syphilis. If the suspected patients cannot be tested symptomatically at different stages in clinical testing, it will lead to missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis. There are many methods for syphilis testing. At present, the more appropriate method for diagnosing syphilis is to refer to the results of serological tests and PCR tests, and combine the history of Treponema pallidum infection to give a comprehensive diagnosis.
More News